English
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-09-08 Origin: Site









When you pick water cooled or air cooled chillers, you see big differences. Each type works in its own way and fits different needs. Water cooled units save more energy. They work best inside buildings. They are good for large commercial spaces. The table below shows why these chillers are popular. They are efficient and small.
| Chiller Type | Market Share (%) | Energy Efficiency Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Water-Cooled | 59.5 | High energy efficiency, compact size, indoor use |
| Air-Cooled | N/A | Smooth at low temps, no water needed in winter |
Water cooled screw chillers cool large areas well. They cost less to keep running. This makes them great for important buildings. Picking the right chiller for your space and weather helps you get better results.
Water cooled screw chillers use less energy. They work well in big buildings. They are good for places that are very hot.
Air cooled chillers are simple to set up. They are easy to take care of. They fit in small spaces. They are best when there is not much water.
Think about costs over time. Water cooled chillers cost more at first. They help save money later on energy and repairs.
Both types need regular care. Water cooled chillers need harder checks. Air cooled chillers need easier care.
Pick the chiller that fits your building. Use water cooled for saving energy. Use air cooled for easy use.
Water cooled screw chillers use less energy. They use cooler water, about 85°F, instead of warm air. This helps them cool water to 44°F with less power. These chillers have better numbers for COP and EER than air cooled chillers.
Tip: Water cooled screw chillers stay efficient in hot weather. They work well even when it is very warm outside.
Variable-speed drives help save more energy. With these drives, chillers can use 25% to 30% less energy. The drive lets the chiller change how hard it works. It uses less power when the load or weather changes.
The table below shows how efficient these chillers are. COP tells you how much cooling you get for each unit of energy. A higher COP means the chiller is more efficient.
| Rated Cooling Capacity (KW) | Minimum COP |
|---|---|
| Less than 528 | 4.10 |
| 528 to 1163 | 4.30 |
| Greater than 1163 | 4.60 |
These chillers use refrigerant to move heat out of a building. The refrigerant goes through the screw compressor. This helps the chiller run quietly and smoothly. These chillers keep working well, even if it gets hotter outside.
Air cooled chillers use outside air to cool the refrigerant. This works best when the air is not too hot. In mild weather, air cooled chillers work well. But when it gets hot, they lose efficiency. The chiller must work harder and use more energy.
You can see the EER for both chillers in the table below:
| Chiller Type | Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) |
|---|---|
| Air-Cooled Chiller | 2.8 |
| Water-Cooled Chiller | 3.5 |
A lower EER means air cooled chillers cost more to run. This is true on hot days. The refrigerant and screw compressor work harder. This can cause more wear over time.
Note: Air cooled chillers do not need water. You can put them outside. They are good for places where water is hard to get.
When you compare both types, water cooled screw chillers save more energy. This is true for big buildings or hot places. Air cooled chillers are easier to install and cost less at first. But you may pay more for energy later. Both chillers use refrigerant and a screw compressor. But they cool the refrigerant in different ways, which changes how much energy they use.
When you look at the price to install a new chiller, you see a big difference between water-cooled and air-cooled models. Water-cooled screw chillers cost more at the start. You pay for extra equipment and setup. Air-cooled chillers have a lower price tag. You can see the numbers in the table below:
| Chiller Type | Initial Cost |
|---|---|
| Air-Cooled | $250,000 |
| Water-Cooled | $340,000 |
If you want to save money at the beginning, air-cooled chillers make sense. Water-cooled chillers need cooling towers and pumps. These add to the cost.
You spend money each year to run and care for your chiller. Water-cooled screw chillers use less electricity. You pay for water, but you save on energy and maintenance. Air-cooled chillers do not need water, but they use more power and need more repairs. The table below shows how much you pay each year:
| Cost Component | Water-Cooled Chiller System | Air-Cooled VRF System |
|---|---|---|
| Annual Electricity Cost | $361,700.00 | $417,000.00 |
| Annual Water Cost | $12,300.00 | – |
| Annual Maintenance | $16,200.00 | $31,700.00 |
| Total Operating Cost | $390,200.00 | $448,700.00 |
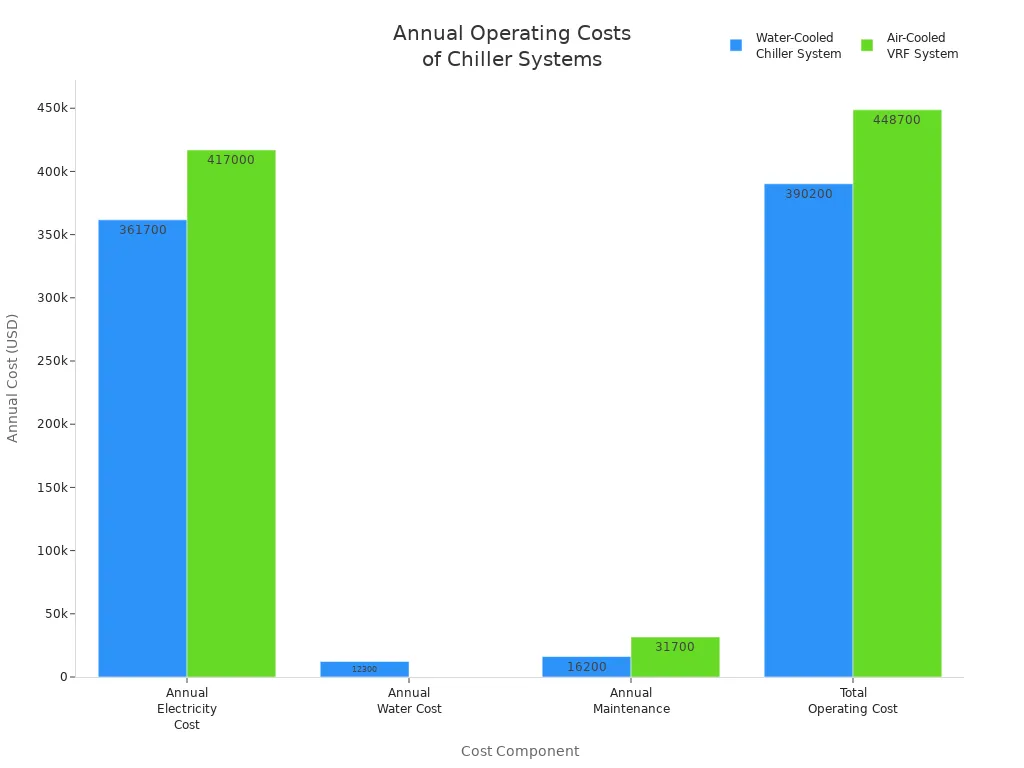
Tip: Water-cooled chillers help you save money over time because they use less energy and need less maintenance.
You want your chiller to last many years. Water-cooled chillers work at lower pressures. They stay inside, away from rain and sun. This means less wear and tear. You pay less for maintenance over the years. Air-cooled chillers sit outside. They face wind, dust, and heat. You may need to fix them more often. Water-cooled chillers give you better value in the long run. You spend less on repairs and get more years of service.
You have to think about space when you pick a chiller. Water cooled screw chillers need more room than air cooled ones. Here are some rules you should follow:
Leave at least three feet on each side and above for service.
Follow all building codes in your area and country.
Keep enough space in front of electrical panels, as the National Electric Code says.
Make sure there is room to take out tubes if you need to change heat exchanger tubes.
Air cooled chillers also need open space around them for good airflow. This helps them work well.
Air cooled chillers are easier to place. You can put them outside. They do not need a cooling tower or extra water parts. This is good if your building does not have much space. Many hospitals and clean rooms use air cooled chillers. They fit in small spaces and do not need much care. Water cooled screw chillers are best for buildings with lots of room for all their parts.
It is harder to install a water cooled screw chiller than an air cooled one. There are more steps and special things you must do. The table below shows what makes water cooled chillers harder to set up:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Location Selection | You need a spot that is flat, easy to reach, and has good air flow for maintenance. |
| Electrical Requirements | The system needs steady power, the right voltage, and its own circuits. |
| Water System Requirements | Clean water, steady flow, and the right pressure stop the chiller from getting too hot or breaking. |
| Piping Installation | Pipes must be the right size and covered to stop leaks and save energy. |
| Refrigerant System | You must put in the refrigerant lines the right way and fill them for good cooling. |
| Structural Support | The chiller is heavy, so you need strong support under it. |
| Safety Precautions | Workers need safety gear and clear signs when installing. |
| Commissioning and Testing | You must test every part after setup to make sure it works right. |
Air cooled chillers are simpler to install. You do not need a water supply or cooling tower. This makes them better for places with little space or time.
You must check your water cooled screw chiller often. Look at it every day to find problems early. Check the temperatures, pressures, and refrigerant levels each day. Always look for leaks when you inspect. Each week, test the water and clean the strainers. Check the oil return and look at the electrical wires. Every month, look at the compressor oil and motor starter contacts. Also, check if the refrigerant has too much moisture. Every three months, clean the water strainers and look at the vanes and bearings. Test the temperature sensors each time you inspect. Every six months, check the capacity control and send oil to be tested. Look at the heat exchanger tubes as part of your list. Once a year, test for refrigerant leaks and do a full oil test. Clean the condenser and evaporator tubes to keep your chiller working well.
| Frequency | Maintenance Tasks |
|---|---|
| Daily | Check and record chiller operating temperatures, pressures, refrigerant levels, and inspect for leaks. |
| Weekly | Test water chemistry, clean strainers, check oil return system, and inspect electrical connections. |
| Monthly | Check compressor oil clarity, inspect motor starter contacts, and check refrigerant moisture content. |
| Quarterly | Clean water strainers, inspect vanes and bearings, and test temperature sensors. |
| Semi-Annual | Check capacity control system, send oil sample for analysis, and inspect heat exchanger tubes. |
| Annual | Perform refrigerant leak test, conduct complete oil analysis, and clean condenser and evaporator tubes. |
You should focus on these main parts when you do maintenance:
Evaporator: Clean the tubes so heat moves better.
Compressor: Use clean oil and check it often.
Condenser: Keep the coils clean so heat leaves well.
Expansion valve: Set it right for good refrigerant flow.
Control panel: Make sure it works right by checking it.
Air cooled chillers are easier to take care of. You do not need to worry about water or cooling towers. Your checklist is about refrigerant, coil cleaning, and checking wires. Look for leaks in the refrigerant circuit and check the compressor. Clean the condenser coils often so heat can leave. Check the expansion valves and control panels to make sure they work right. If you check often, you can stop breakdowns. Air cooled chillers take less time to maintain, but you must watch for leaks and blocked coils.
The type of chiller you pick changes how long it lasts. Water cooled screw chillers last 20 to 30 years. Air cooled chillers last 15 to 20 years. You can see the average life in the table below:
| Chiller Type | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Air-Cooled | 15 to 20 years |
| Water-Cooled | 20 to 30 years |
If you follow the checklist and check your chiller often, it can last longer. Water cooled screw chillers stay inside, so they do not get damaged by weather. This helps them last more years. Air cooled chillers sit outside, so they get sun, wind, and dust. You may need to fix them more often. Good maintenance keeps your chiller healthy and helps it last longer.
Pick a water cooled screw chiller if you need strong cooling for big spaces. These chillers are great when you want to save energy and money over time. They work well in large buildings or places that need lots of cooling. You get the best results with this type of chiller.
Here is a table that shows where water cooled screw chillers are best:
| Type of Building | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Commercial Buildings | Saves energy and keeps people comfortable inside. |
| Data Centers | Gives strong cooling and uses less power, saving over 30%. |
| Food Processing Plants | Helps keep food cold and makes work smoother. |
| Hospitals | Gives steady cooling for patients and medical tools. |
| Hotels | Quiet and efficient cooling for guests. |
| Large Offices | Keeps the temperature steady for many people and devices. |
Note: Water cooled chillers are good for hospitals, hotels, and big offices. They keep things cool even when it is hot outside.
You also see these chillers in schools, malls, and factories. They work best where you can put in cooling towers and have enough water. If you want your building to run well and save on bills, this chiller is a smart pick.
Air cooled chillers are best where water is hard to get or you want a simple setup. You do not need a cooling tower or extra pipes. This makes them easy to put in and take care of. If your building is small or you do not have much space, these chillers are helpful.
Look at the table to see where air cooled chillers work best:
| Application Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Commercial Buildings | Good for cities where you cannot use a water tower. Handles normal cooling needs. |
| Residential Complexes | Works in tall apartments where water systems are hard to build. |
| Small and Medium-sized Facilities | Keeps smaller factories cool and does not use much energy. |
| Data and IT Centers | Keeps servers safe where water is not easy to find. |
Air cooled chillers have some limits in big buildings.
They do not cool as well as water cooled chillers in hot weather or big spaces.
They wear out faster because they sit outside in the sun, wind, and rain.
They can be loud, which may bother people in big offices.
Tip: Choose an air cooled chiller if you want fast setup, lower cost at first, and do not have much space or water.
If you have a small office, shop, or data center in a dry place, this chiller gives you steady cooling without needing extra water.
It is important to think about water use when picking a chiller. Water cooled screw chillers need a lot of water each day. This can make your water use very high, especially in dry places. Local water rules can be strict about how much water you use. You have to watch your water use to follow these rules.
Water cooled chillers might use thousands of gallons every year.
Some cities want you to tell them how much water you use for cooling.
Water from chillers can get dirty or have chemicals. You must clean this water before letting it go to stop pollution.
If you do not have enough water or cannot clean it, you could get fined or have other trouble. Air cooled chillers do not use water, so you do not have these problems. You can pick air cooled models if you want to use less water.
You also need to think about noise and emissions when choosing a chiller. Water cooled screw chillers are usually inside buildings. They are quieter than air cooled chillers. This helps keep your work area calm and nice. Air cooled chillers are outside and use fans. These fans can be loud, especially when it is hot.
Both chillers use a refrigerant to move heat out. The refrigerant system cools your building. You should check for leaks in the refrigerant lines. Leaks can let out gases that hurt the environment. Some refrigerants can cause global warming or harm the ozone layer. You should pick chillers with safer refrigerants and follow safety rules.
Water cooled chillers often use less refrigerant because they work at lower pressures.
Air cooled chillers may need more refrigerant to work well when it is hot.
You should check the refrigerant system often to stop leaks.
Tip: You can help the planet by picking chillers with low-emission refrigerants and keeping your system working well.
You can spot big differences between water cooled and air cooled chillers. The table below shows the main things to know:
| Feature | Water Cooled | Air Cooled |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Water Use | High | None |
| Maintenance | More complex | Simpler |
Water cooled chillers are best for big buildings in hot places. They help save energy when that is important. Air cooled chillers work well in small spaces or where there is not much water. Think about how much energy, money, and water you want to use before you choose.
Water cooled chillers use water to remove heat. Air cooled chillers use air. Water cooled chillers work better in big buildings. Air cooled chillers fit small spaces and do not need water.
Water cooled chillers last 20 to 30 years. Air cooled chillers last 15 to 20 years. You get more years from water cooled chillers because they stay inside and avoid weather damage.
Yes, water cooled chillers need thousands of gallons each year. You must check local water rules before you install one. Air cooled chillers do not use water.
Air cooled chillers can be loud because they use fans outside. You may hear them if you stand near the unit. Water cooled chillers run quieter inside buildings.
Tip: Pick water cooled chillers for large buildings and hot climates. Choose air cooled chillers for small spaces or places with limited water. Always think about your budget, space, and local rules.
